Glasgow City Region
Income deprivation across Glasgow City Region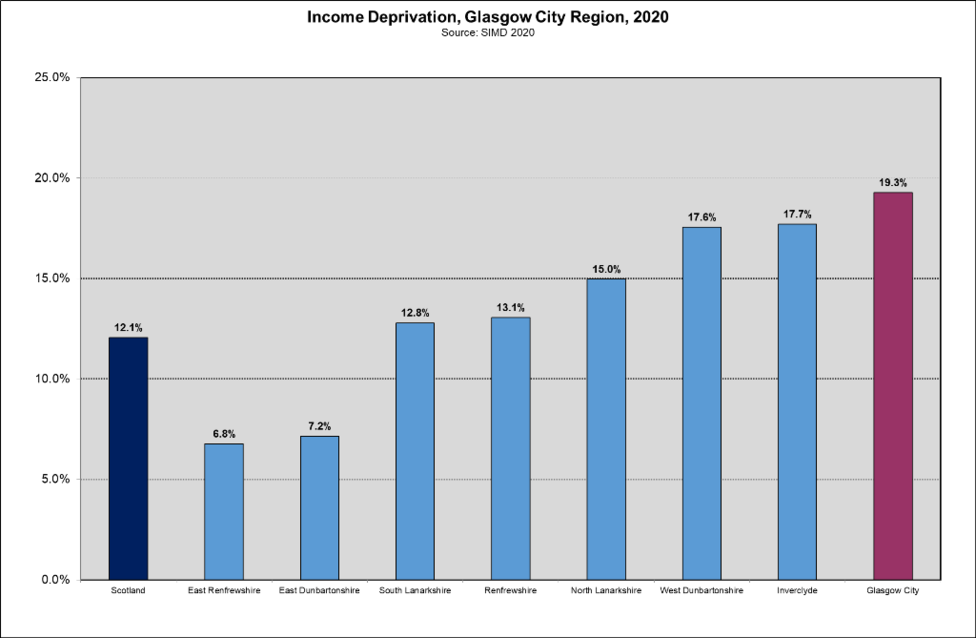
Despite recent reductions in deprivation in the city, Glasgow still has the highest level of income deprivation among the eight local authorities within the Glasgow City Region. In Glasgow, nearly a fifth of the population (19.3%) are living in income deprivation compared to 7.2% in East Dunbartonshire and 6.8% in East Renfrewshire.
Employment deprivation across Glasgow City Region

Despite recent reductions in deprivation in the city, Glasgow still has the second highest level of employment deprivation (13.3%) among the the eight local authorities in Glasgow City Region; Inverclyde has the highest level of employment deprivation (14.3%). The lowest rates of employment deprivation in GCR are in East Renfrewshire (5.6%) and in East Dunbartonshire (6.2%).
Notes
Income deprivation - as defined by the Scottish Index of Multiple Deprivation (SIMD), is a measure of the percentage of the population (adults and their dependents) in receipt of Income Support, Employment and Support Allowance, Job Seekers Allowance, Guaranteed Pension Credits, and Child and Working Tax Credits.
Employment deprivation - as defined by the Scottish Index of Multiple Deprivation (SIMD), is a measure of the percentage of the working-age population (men aged 16-64 and women aged 16-60) who are on the claimant count, receive Incapacity Benefit, Employment and Support Allowance, or Severe Disablement Allowance.
SIMD - Scottish Index of Multiple Deprivation provides a relative measure of deprivation based on indicators from seven domains – income, employment, health, education, access, housing, crime. The index identifies multiple deprivation for 6505 small areas (data zones) across Scotland. There have been five versions of SIMD to date. The initial index of 2004 (SIMD 2004) has been revised five times in 2006 (SIMD 2006), 2009 (SIMD 2009), 2012 (SIMD 2012), 2016 (SIMD 2016) and 2020 (SIMD 2020). More information is available on the SIMD site.
